这是spring源码阅读的第一篇文章。其实spring源码的入口有很多。
新建一个空的maven项目,然后在pom文件导入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
spring入口方式
自己创建的demo使用了两种方式来创建spring容器:
- 使用xml文件配置的形式
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/quickstart-byname.xml");
Red bean = context.getBean(Red.class);
- 使用Java的config形式
ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringScanConfig.class);
Blue bean = context.getBean(Blue.class);
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.test.spring")
public class SpringScanConfig {}
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext入口
下面我就用第二种方式作为spring源码的入口,还得指定一个配置文件,为了自动注入,配置文件加上了@ComponentScan("com.test.spring")这段代码, 目的是为了让spring去自动发现与注入,不用手动注册bean,当然,也可以在配置文件中手动注册bean信息。 来看看AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的类继承图:
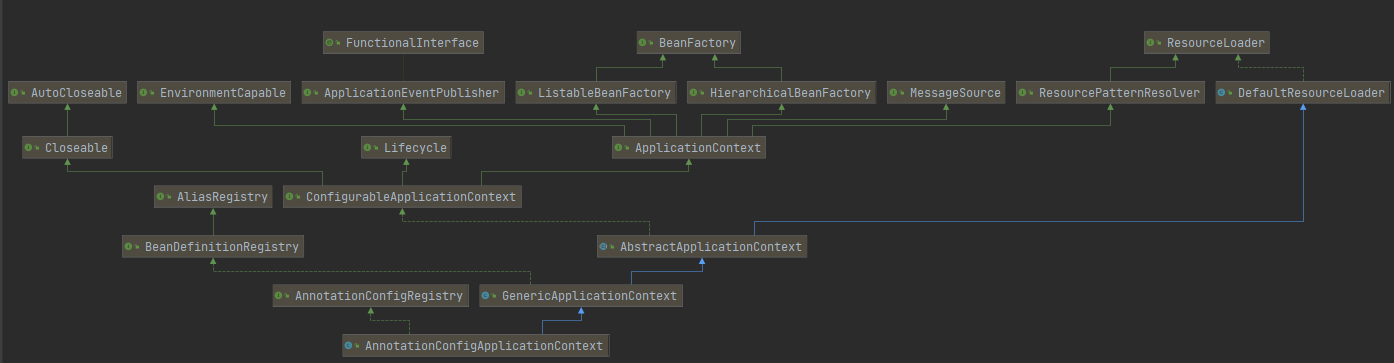
根据继承图,来看看他们分别干了什么;
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext: 无参构造方法分别给reader和scanner赋值
- GenericApplicationContext: 给beanFactory属性赋值
- AbstractApplicationContext: 给resourcePatternResolver属性赋值
- DefaultResourceLoader: 给classLoader属性赋值
下面看看用部分源码:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
// 构造方法
this();
// 注册类信息
register(componentClasses);
// 刷新 重点
refresh();
}
AbstractApplicationContext.refresh();
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 为刷新准备上下文
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂,获取bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 准备bean工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 准备beanFactory完成后的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 执行beanFactory后置处理(所有的bean信息将在这个地方注册进beanFactory中)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册bean后置处理
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件控制器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 初始化其他特别的bean信息
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化所有非懒加载的bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 完成容器创建
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// 清除缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
这就是一个spring容器创建的大概流程,一个spring容器的创建还是挺复杂的,涉及到了方方面面。 后面的笔记在来对其中的一些流程进行详细的分析。


